What is the risk?
Risk is the possibility of losing planned values or sometimes a threat to/from unseen damage, injury to the intended outcomes. This is completely uncertain, however, in a few cases, it can be avoided through preemptive actions. Risks are basically of different types based on the situation the project is in.
Monetary transactions are related to financial risk whereas uncertainty in business leads to business risk. So as a whole we can find a risk (uncertainty) in each and every activity involved.
Examples of risks and its consequences:
Risk of Budget: Budget risk relates to the finance of the project. Due to that the project is not properly managed and delivered. It leads to the time delay of the project.
Scope creep/unclear requirements: Client expectations are getting changed again and again during the course of project execution. It leads to delay of the project and overall quality of the project. It’s also seen that the client expectation was watermelon and the delivered product was guava (Here client requirement is a fruit with a lot of seeds inside it and color inside the fruit is red). It creates a bad relationship between the client and vendors.
Architectural Risk: If the design is not correct and extremely complex, the team is not able to understand and delivers the inappropriate product. The regression impact is more and the project is overloaded with lots of defects.
Risk of people: Not getting the right people at the right time is a risk. If people are not well experienced, they introduce a lot of bugs in the project code. So delivery quality will be on stake.
When we think of any risk during project execution, it always leads to the unhappiness of the clients. It costs the company's reputation and relation with the client. Clients basically do not want to get involved in any of the risks, on the other hand, they want to know the steps project team has taken to mitigate the risk.
In order to avoid this, the project team uses risk management processes and without managing risk we can say “this is a risk of not implementing risk-management in a project “
What is the management of risk?
Management of risks points to the process of identifying, accessing and controlling of the threat to/from uncertainty. This process enables the overall risk to be understood and managed proactively so that the threats will be minimized and the opportunities or outcomes are maximized. All projects are prone to risk considering their uniqueness. They are also based on some assumptions which are Boolean in nature. If the assumption is right there will be less risk and if it’s wrong, the chances of risk are very high. Risk of IT projects also follow the same path. It cannot be completely avoided but it can be managed to lower its impact.
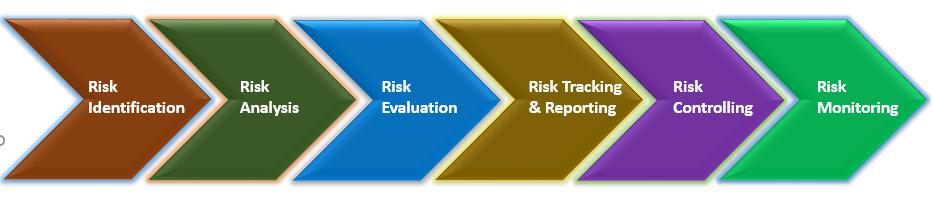
The basic process to manage the risk is given below: Risk management steps
1. Identifying the Risk:
The first step towards risk management in a project is to identify the risk. The project teams follow a couple of techniques to identify them at the early stage. Below is the list of few techniques which are followed nowadays
Brainstorming or a common discussion: In this discussion the PM and the team members go through different questions and suggestions. They also discuss the objectives of the projects. Based on the objectives of the projects, the related risks are thought of. The significant risks may be related to scope, budget, and timelines. Sometimes thinking the obvious risks which can go wrong, maybe a right practice. This comes from the experience of the people belonging to a certain domain, technology, and business. These brainstorming questions may include people, quality, availability, resource-related risks.
Learning from past experience: Before starting any project, the project team needs to check if the organization has any common list of risks which they had faced in the past. Those should always be documented for future use. After the project ends, there should be project reviews to capture the most important risk. All organizations use to keep a list but if it's not available we need to make sure to create such a list of future. When the project starts with all new sets of people in the team, they should go to some other team of the same domain to get the expert review on that. The expert can share their experiences with the most occurred risks so that these can be avoided in the new projects.
Assumptions: Assumptions play a vital role in identifying the risks. Correct assumptions tend to reduce the risk whereas wrong assumptions lead to hazard which may damage the overall objective of the projects. So all the assumptions must be discussed, captured and documented. Sometimes becoming pessimistic is also very helpful. It will allow us to think the maximum negative impact on any risk occurring in the project.
Diagrams/techniques: Nowadays project teams follow some diagrammatic presentations like a cause-effect diagram and affinity diagram. The output of these diagrams/techniques is to prioritize the risks. Once we got to know these techniques the identification of risk will be faster. The affinity diagram is a fun activity to discuss with the team, get the risks and list in the category with funny titles.
Analysis of customer complaints: Sometimes the feedback received from the customer is a valuable point in identifying risk. It enables the project team to know what is wrong. Based on the feedback the project team can work to get those issues corrected.
Strategies use to identify risks: Business methodologies like flow charts, SWOT analysis, and some kind of simulations may help in identifying the risk. Risk identification must be an ongoing process of the life cycle of any project but it should be performed and validated at the early stage of the project. (It may be projected intake stage or in the planning stage).
2.Analyze and prioritize the risk:
Once the risks are identified they must be analyzed to find out the severity and the possibility to occur. The risks of high severity and more occurrence can be treated with high priority and need all stakeholders’ attention, however low severity risks can be managed with less attention. If a risk is expected to occur most of the times then its impact is very high in terms of its management. It's an extreme condition for the project and needs immediate action. On the other hand, if the risk is rarely occurring and it's felt that it is of low severity, it can be managed by the routine activities of the project.
3. Evaluation of risk and its impact:
This is the process of quantifying the impact on each risk. Once the risks are identified and analyzed, the project team has to evaluate the risk to find out the corrective actions. Two ways to measure the risk are the Qualitative and Quantitative risk validations. Qualitative risk evaluation helps in getting the possibility of risk and its impact whereas quantitative evaluation helps in providing more data to make decisions on corrective actions. The main reason to evaluate the risk is to prioritize its occurrence and impact. It's not always possible to manage all risks at the same time. So once the risk is evaluated, it helps in identifying us was to use our limited time and effort. Rest of the things can be mitigated through a regular course of action. Sometimes it’s seen that 30 percent of risk creates a 70 percent of the impact. The bigger the risk, the higher the order for its evaluation.
4. Tracking and reporting of the risk:
All the risks must be tracked and documented on a regular basis. This will help in avoiding such risks in the future and finding a way to mitigate before they actually occur. The course of action can also be documented for the risks to be addressed. It also helps the stakeholders know about what is happening to the project. A risk register, sometimes known as a risk log, is an important component of the overall risk management framework. This is created during the early stages of a project, a risk register is a tool that helps you track issues and address them as they arise. Basically, it's a log that identifies risks along with their severity and the actions and steps to be taken to mitigate the risk. Project managers used to review these and monitor the risks associated. Based on this they use to take necessary actions.
5. Controlling the risk by taking necessary steps:
Known risks can never be eliminated, rather they can be controlled to lower the impact if planned. Unknown risks are sometimes handled but it takes time to understand and make some mitigation plan. The only way of/for controlling risk is to accept that and take necessary action on that. If we neglect to accept the risks it will be moving into a hazard and the project will go into failure track.
6. Continuous monitoring of the managed risks:
This is the process of monitoring the managed risk and also to identify new risks. Risk monitoring is the process of information gathering from manual interventions, alerts, and automated systems. It gives inputs to ongoing risk assessment and response processes. Risk monitoring is also recommended based on the severity of the risk. If the risk is very severe it should be monitored with utmost priority. All level of risks are monitored but not in a constant manner and some of the onetime risks are not required to monitor also. It lets us know the risk as soon as it starts. There will be no delay in taking the corrective action in planning and mitigation of the risk.
The consequences of risk are not appropriate for any project. So risks are fine as soon as project teams find it and mitigate, but it’s really a risk of not implementing risk management in projects.
Exclusive pmmagazine.net 💬
Asit Chandra Dash
About author
Manager Program Management on Digital transformation, at Sapient
Asit Chandra Dash
Manager Program Management on Digital transformation, at Sapient
Total Articles: 6Crisis Management 1 Emotional Intelligence 1 AI and Automation 1 Stakeholder Management 1 Risk Management 1 General 1